Arsenic is known to be a deadly poison, often found in pesticides and herbicides. Therefore, it is no surprise that arsenic-contaminated water is a problem that needs to be addressed immediately. Join Song Phung to learn about the risks of arsenic, how to test water for arsenic, and how to remove it.

What is arsenic?
Arsenic is a naturally occurring semi-metal that is highly soluble in soil, rock, or water. Groundwater is contaminated with inorganic arsenic through natural deposits and other forms of pollution. For example, pesticides can settle and leach into nearby groundwater. Factories discharge inorganic arsenic into the environment at high rates and rainwater carries it into groundwater. Wells near natural deposits, industrial, mining, or agricultural sites are susceptible to arsenic contamination.
Many studies have shown that groundwater in the Red River and Mekong Delta regions is at high risk of arsenic contamination. Many wells in the Red River basin such as Ha Tay, Ha Nam, Hanoi, Nam Dinh, Hung Yen and Thai Binh have high arsenic levels of about 200–300 µg/l (20–30 times higher than drinking water standards).
Risk of Arsenic Poisoning
If you use well water, you are at risk of some of the negative effects of exposure to Arsenic. Although you may not get acute arsenic poisoning, you may experience some health problems later on. According to widely published data from the World Health Organization (WHO), for every 10,000 people who get cancer, 6 die from drinking water with arsenic concentrations higher than the WHO standard of 0.01 mg/liter.
Arsenic in drinking water
Arsenic has been detected in groundwater in all 48 contiguous states. No matter where you live, inorganic arsenic may be present in your tap water. According to standards in Vietnam QCVN 01:2009/BYT: NATIONAL TECHNICAL REGULATIONS ON DRINKING WATER QUALITY and many other places in the world: 0.01 mg/liter is the amount of arsenic allowed in water. Some studies show that even very small doses of arsenic increase the risk of diabetes and cancer. So it is best that drinking water does not contain arsenic.

Arsenic in drinking water
Water used for cooking and domestic use is considered safe with an arsenic content of less than 0.05 mg/liter. Inorganic arsenic is not easily absorbed through the skin upon contact. However, children can easily absorb arsenic when water gets into their mouths when bathing or swimming, so adults need to supervise this process.
Arsenic in well water
The most dangerous levels of arsenic are found in well water. Because private wells are not closely monitored by government agencies, they can contain dangerous levels of arsenic. Inorganic arsenic enters well water through natural sediments, industrial waste, and agricultural products such as pesticides and herbicides. In areas with industrial pollution, rainwater can absorb arsenic from the air and carry it into groundwater, contaminating wells. Fertilizers, animal feed, and pesticides can also leach inorganic arsenic into groundwater. Fortunately, testing for arsenic in water is a simple process.
How to test water for Arsenic?
Arsenic test kits are quick and effective. These test kits are easy to use, and many provide results in as little as 12 minutes. First, you mix water with a tartaric acid reagent. Next, you add an oxidizing reagent to the mixture to eliminate the interference of hydrogen sulfide. Finally, you add a third reagent, zinc powder, to convert the inorganic Arsenic into Arsine gas. The test strips inside the kit then measure the level of Arsine gas in the water mixture.
Why is it necessary to remove Arsenic from water?
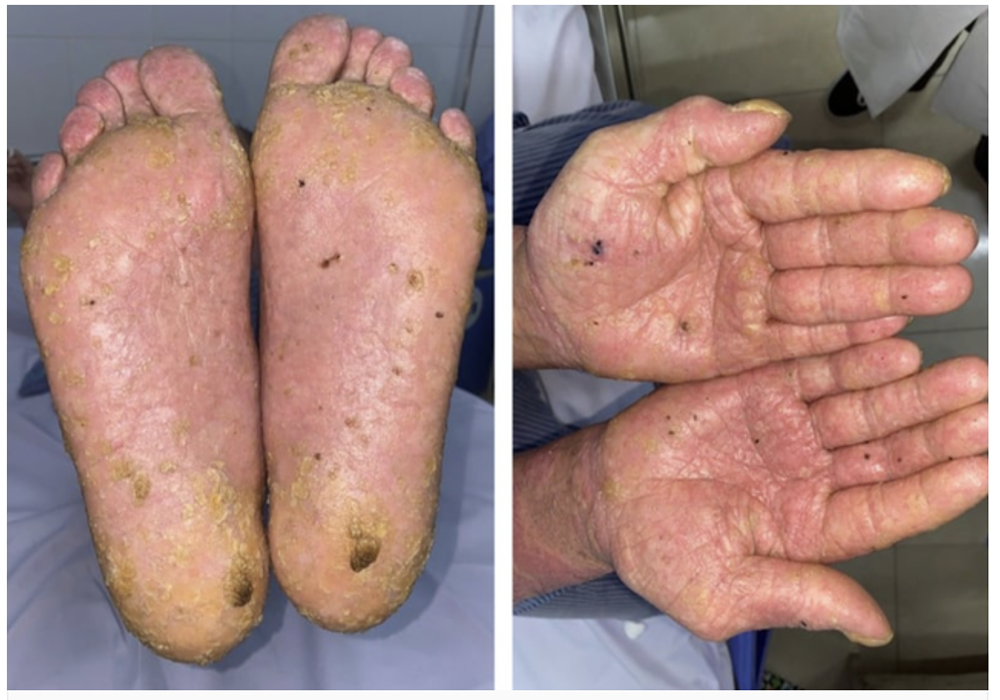
In high enough doses, inorganic arsenic can be fatal. Long-term exposure to low levels of arsenic increases the risk of both diabetes and cancer. Symptoms associated with arsenic poisoning include nausea, diarrhea, cramps, and numbness in the extremities. If your water contains small amounts of arsenic, you may not experience any of these symptoms, but your long-term health is still at risk.
What are the best methods to remove arsenic from water?
Arsenic exists in water in many forms and its toxicity depends on the form in which it exists. Inorganic arsenic is primarily found in two different oxidation states, Arsenic III (As3) and Arsenic V (As5). Due to its high solubility in water, As3 is significantly more toxic than As5. If As3 is present in water, treating the water by converting As3 to As5 allows for more arsenic to be removed in the final treatment. The most common process for converting As3 to As5 involves oxidation with chlorine.
The most effective methods of removing arsenic from water are ion exchange, reverse osmosis, and distillation.
Ion exchange
Ion exchange is a process used to soften water and deionize, removing contaminants from water. The ion exchange process uses resin beads to remove most of the Arsenic from water. However, this method requires regular maintenance. About every 3 months, you need to add salt to the salt tank so that the softener system can draw salt into the ion exchange resin beads to maintain the water filtration efficiency. This method is often used to treat well water.

Advantages of ion exchange
- Thorough and selective treatment (successfully removes positively charged metals such as Zn, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, Hg, Cd, Mn, cyanide compounds, arsenic, phosphorus, radioactive substances)
- Allows recovery of fine metal components
- Low energy consumption
- Long life of ion resin beads
Disadvantages of ion exchange
- Do not remove impurities or bacteria from water, so they are often paired with other filtration systems to reduce sediment and dirt
- In the unlikely event of valve failure, some As5 may be released into the treated water
- Needs regular maintenance
- Discharge a quantity of salt into the environment when regenerating the ion exchange softening column
Distillation
A distiller works by heating water, collecting the steam, and cooling the steam down to a liquid state. When the water is boiled, impurities that have a higher boiling point than the water are left behind because they cannot evaporate. The evaporated water is then cooled and drips into a collection tank. The distiller removes dissolved minerals and heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, and mercury.

Unlike ion exchange and reverse osmosis systems, distillers are not systems that can be used continuously. Rather, home distillers are countertop systems that must be filled with water manually. In the home, distillers are typically used only for drinking and cooking because the distiller cannot be hooked up to a faucet or the home’s water supply.
Advantages of distillation
- Distillers remove pathogens and heavy metals from water, reducing the risk of illness from drinking water.
Disadvantages of distillation
- Distillers cannot be hooked up directly to a water source. Instead, they are filled manually and can only produce a small amount of water at a time/
- Because they require a source of energy to be heated, distillation equipment is more expensive to operate and less environmentally friendly than other methods.
- Removing chemicals that have similar boiling points to water can be difficult with a distiller. Precise pressure and temperature are required to remove as many impurities as possible.
- Distillers require regular maintenance. Minerals build up in the boiling chamber over time and if not cleaned out will affect the performance of the machine.
- Distillation removes minerals and reduces the amount of oxygen in the water.
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) treats water by forcing pressurized water through a semi-permeable membrane. This process removes sodium, chloride, copper, lead, arsenic, and many other contaminants. RO systems remove As5 at a higher rate than As3, making pretreatment important for best results.
RO systems are typically point-of-use (POU) systems that attach to a dedicated faucet. POU RO systems allow filtered water to be used for drinking, cooking, and ice making. These systems typically produce only 7-80 liters per hour.
For well water contaminated with arsenic, point-of-entry (POE) RO systems are still a worthwhile option. POE RO systems allow you to use filtered water for all applications around the home, such as showering and gardening. In many cases, RO is a good method for removing As3.

Advantages of reverse osmosis
- RO removes over 90% of bacteria, combined with UV ultraviolet lamp equipment; treated water no longer has viruses and disease-causing bacteria, absolutely safe to use.
- RO removes all harmful substances and chemicals found in groundwater, river water, surface water…
Disadvantages of reverse osmosis
- Sediment can reduce the efficiency of the pre-filters of the RO system and chemicals can damage the RO membrane, too much residual chlorine in tap water also damages the RO membrane.
- RO systems are used to filter treated water and are not designed to treat raw well water.
- RO removes mineral content from water.
See more: Worry Of Iron Bacteria Existing In Water
Having been present in the market for more than 10 years, Song Phung is proud to be a supplier of optimal products and solutions for household and production water sources. Contact our Hotline 0913.90.72.74 – 0984.620.494 to get a product quote, or order online quickly at https://thietbinganhnuoc.com/san-pham
Follow Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/SongPhungthietbinganhnuoc/ to be updated with new products.