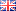
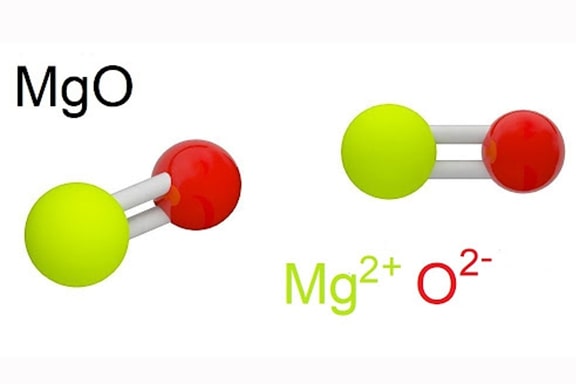
Each tiny MgO particle has miraculous applications from industry to medicine. Have you ever wondered “what is Mgo” and how can it improve our quality of life? Let’s explore the mysteries of magnesium oxide (MgO) – from its outstanding properties, complex production process to a series of unexpected applications in daily life. Let’s learn about this potential material with Song Phung Water Equipment!
What is magnesium oxide (MgO)?
Magnesium oxide (MgO) is a chemical compound composed of magnesium and oxygen. Magnesium oxide is produced by heating magnesium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide. It is one of the most common compounds and plays an important role in many industries and medicine.

Unique properties of Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Before delving into the practical applications of MgO, let’s learn about the outstanding properties that make this compound so versatile.
Physical properties
- Color: white
- Solubility: Soluble in: water, acid, ammonia, insoluble in alcohol
- Molar mass: 40.3044 g/mol
- Specific volume: 3,58 g/cm³
- Solubility of MgO in water: 0,0086 g/100 mL (30°C).
- Melting point: Magnesium oxide has a melting point of about 2,852 degrees Celsius (3.125 K; 5.166 °F). Because of this property, MgO is often used in applications that require heat resistance.
- Boiling point: 3,600 degrees C (3.870 K; 6.510 °F).
- Insulating properties: Magnesium oxide has good electrical insulating properties. The insulating properties of MgO make it an ideal material for the production of insulating components for electrical and electronic equipment.
Chemical properties
MgO is a basic oxide (alkaline earth oxide), so it is a strong base and exhibits the typical reactions of basic oxides.
- Reacts with acids: MgO reacts with strong acids to form salt and water. For example:
2HCl + MgO ⟶ H2O + MgCl2
- Reaction with water: MgO can react with water to form magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂), however this reaction usually occurs at high temperatures (100-125°C):
H2O + MgO ⟶ Mg(OH)2
- Reaction with other oxides: MgO can react with other acidic or alkaline oxides to form salts or complex compounds. For example:
2CaO + 2MgO + FeSi ⟶ Fe + 2Mg + Ca2SiO4
Magnesium Oxide Production Process (MgO)
The production process of Magnesium Oxide (MgO) starts from natural sources such as dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) or seawater, which contains magnesium. The production of MgO requires close coordination between many stages, from raw material extraction, conversion, refining to final product quality control. Below are the detailed steps in the MgO production process based on reference materials:
Phase 1 – First is Raw Material Extraction
Dolomite is a mineral containing magnesium and calcium, mined from natural quarries. The process of mining dolomite involves mining, transportation, and initial processing to remove impurities.
Magnesium can also be extracted from seawater through evaporation and chemical extraction. Seawater contains about 0.13% magnesium, and the extraction process requires the removal of water and other impurities to obtain magnesium chloride (MgCl2).
Phase 2 – Transformation
Dolomite is heated at high temperatures in a rotary kiln to decompose into magnesium oxide and calcium oxide.
Magnesium chloride from seawater is converted to magnesium oxide through electrolysis or heating. In electrolysis, an electric current is used to split MgCl2 into MgO and chlorine gas (Cl2). In heating, MgCl2 is heated at high temperatures to produce MgO and hydrogen chloride gas (HCl).
Phase 3 – Refining
After the conversion process, the resulting MgO may contain impurities and needs to be refined to achieve high purity. The refining process includes steps such as washing, filtering and re-calcination to remove impurities.
The MgO is washed with water and chemical solutions to remove soluble impurities. The MgO is then filtered to separate insoluble particles.
The washed and filtered MgO will be re-calcinated at high temperature to ensure all impurities evaporate or decompose, increasing the purity of the final product.
Stage 4 – Crushing and grading
After refining, MgO is ground into fine powder to suit different usage requirements. The grinding process increases the surface area of MgO, making it easier to react and use in industrial applications.
After grinding, MgO will be classified according to particle size to ensure uniformity and compliance with technical standards. Classification is done by sieves or particle classifiers.
Stage 5 – Final Quality Control
The final MgO will be quality tested to ensure it meets technical standards and usage requirements. Testing includes checking for purity, particle size, and other physical and chemical properties.
After quality testing, MgO will be packaged in specialized packaging for storage and transportation. MgO needs to be stored in dry conditions, avoiding contact with moisture to maintain quality.
The production of MgO involves many complex steps and requires strict supervision to ensure the quality of the final product. From the extraction of raw materials, through the conversion, refining, grinding and grading steps, to quality control, each stage plays an important role in producing high-purity Magnesium Oxide (MgO) suitable for industrial and medical applications.

>>> See more: What is arsenic? What are its harmful effects and dangers to health?
Applications of MgO
Applications of MgO (Magnesium Oxide) are very diverse in many fields such as industry, agriculture, environmental treatment and medicine:
Applications in environmental treatment
- Wastewater treatment: MgO is used as an adsorbent to remove heavy metals, phosphates, nitrates; increase pH and adjust alkalinity of wastewater, helping to increase treatment efficiency.
- Water softening: MgO helps remove calcium and magnesium ions that cause water hardness, prolonging the life of equipment and water filtration systems.
- Soil and groundwater treatment: MgO stabilizes pH, neutralizes acid or alkali in soil and water, minimizing adverse impacts on the environment and human health

You may be interested in:
Improve air quality
MgO is also used in industrial waste gas treatment, helping to absorb pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
In industrial production
Magnesium oxide is widely used in industries, from the production of refractory and insulating materials to cement and fireproof materials.
Heat-resistant, insulating material
- Metallurgy: MgO is used as an anti-corrosion and slag forming agent in blast furnaces producing steel, cast iron, and non-ferrous metals. It helps absorb impurities and improve metal quality.
- Refractory material: Is the main component of refractory bricks used to line blast furnaces, iron and steel furnaces, glass and cement furnaces thanks to its ability to withstand high temperatures, be fireproof, termite-proof, moisture-proof and increase the durability of building materials.

Cement
MgO is also an important ingredient in cement production. It helps improve the durability and water resistance of cement, while minimizing shrinkage and cracking as the cement dries.

More research: Is Wastewater Treatment Yeast Really Effective?
Fireproof materials
MgO is used as the core in fireproof, heat-resistant Magnesium Oxide Board (MGO) panels, used in ceilings, partitions, floors, suitable for houses, apartments, offices, and commercial centers.

Fertilizer
In agriculture, MgO is used as a fertilizer, providing a source of magnesium necessary for plants. Magnesium is an important trace element, helping plants photosynthesize and grow healthily. In addition, MgO helps neutralize acid in the soil, creating a favorable environment for plants to absorb nutrients.

Medical applications
Magnesium oxide not only plays a role in industry but also has many important applications in medicine. The use of MgO in pharmaceuticals and medical products brings many benefits to human health.
Magnesium oxide plays an important role in medicine, especially in the production of drugs. MgO is used as an ingredient in antacids, which help relieve symptoms of indigestion and stomach pain.
Note when using: MgO can cause side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, or allergies in some people. Therefore, it is very important to follow your doctor’s instructions and read the instructions carefully before using.

Magnesium oxide (MgO) is truly a versatile compound with many important applications in life and industry. Understanding the properties, production process and applications of MgO will help us make the most of the benefits that this compound brings. Hopefully the above information provided by Song Phụng Water Equipment has helped answer some of your questions about “What is Mgo?”.
>>> Services for you::
- Quotation and consultation for professional water treatment system installation at Song Phung